
Usage and distribution for commercial purposes requires written permission.
#Checkmate 649 license
This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC).
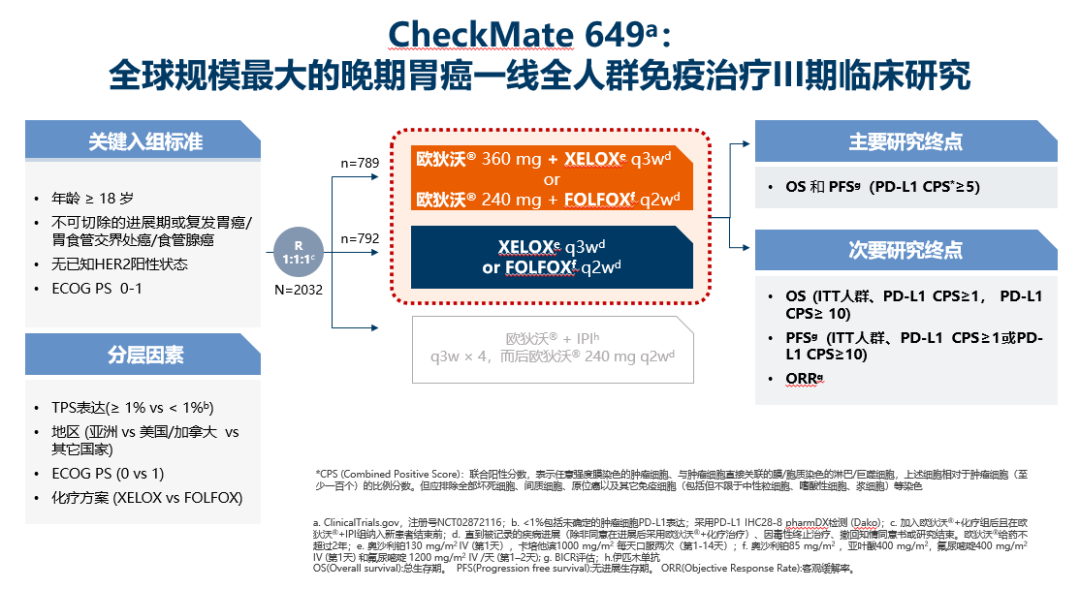
Open Access License / Drug Dosage / Disclaimer Key Message: In this review, we highlight recent improvements in the treatment landscape of advanced gastric cancer, the heterogeneity of this disease, and possible personalized targets. Nonetheless, the impact of immunotherapy combinations and immunochemotherapy remains an area of investigation. Recent first-line data show a significant survival benefit in aGC patients with a CPS ≥ 5 under immunochemotherapy. Furthermore, immuno-oncology with checkpoint inhibition and immune stimulation has evolved in the field of aGC. As such, ramucirumab has led to significant and clinically meaningful advancements in the second-line treatment. The addition of monoclonal antibodies has substantially improved outcomes in this setting. Unfortunately, almost all patients who receive first-line treatment (with or without anti-HER-2 blockade) progress and <70% are eligible for a second-line therapy. Triplet combinations adding taxanes to the doublet regimen are reserved for certain scenarios.

A combination of platinum and fluoropyrimidine remains the first-line chemotherapy backbone in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer. Various examples like the application of trastuzumab in the HER-2-positive subgroup underline the benefits of this approach starting from the first-line setting. Molecular profiling (at least for HER-2-expression, microsatellite instability status, Epstein-Barr virus expression, and programmed death ligand-1 expression/combined positive score ) is recommended for all therapy-fit patients prior to the start of a systemic treatment and is crucial for decisions on treatment strategy and drug selection. Summary: Systemic treatment options for advanced gastric cancer (aGC) have evolved over the recent years, implementing the growing molecular knowledge of this heterogeneous disease. Several treatment possibilities have been investigated, but only a few show clinically meaningful results. Background: Gastric cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
